Utilization Methods for Sensor Information as Learned from IoT Success Stories (Sensors and IoT devices Column Part 3)
Last time, in Part 2, we explained how to select the right IoT gateway device, with the title “Focusing on Sensor Interfaces: Fail-Proofing Your Choice of IoT Gateway.” In this part, Part 3 (the final part), we will review how to use sensor information, before going on to explain some IoT success stories and IoT systems provided by CONTEC by giving a few examples, while also touching on information linkage with other IT systems, and how to utilize closed networks and the cloud.
How to Use the Collected Sensor Information
Before explaining various successful IoT case studies we have collected, let’s examine the method of using the collected sensor information. The following table lists the types and usage examples of sensors used for various measurement targets, and examples of output signals.
The sensor used for the specific measurement target collects a lot of information. Because sensor information is output with a variety of signals, in order to use different types of sensor information it is key to install devices that can easily handle different types of output signals.
CONTEC’s products can handle a variety of output signals together, enabling connection with network servers without the need to create programs.
If you’re really not sure about the sensor types or how to use them, see “Part 1: IoT Sensor Types and Applications.”
Uniform Management of Operation Status and Abnormality Detection by Using the IoT for Existing Factory Equipment
As an example of successful IoT usage with sensor information that shows multiple output signals, allow us to introduce the uniform management system for operation status and detection of abnormalities by “changing over to IoT with existing factory equipment (production line).” The following is an overview of the system we are describing.
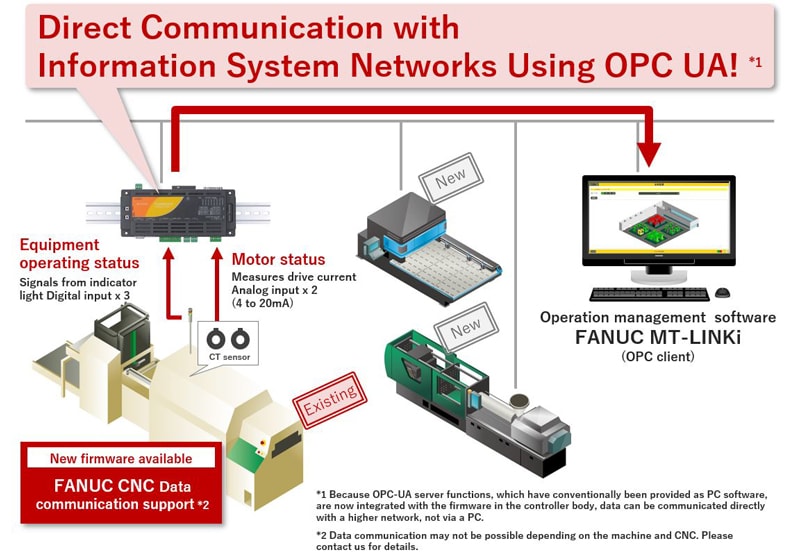
With machine equipment motors, by installing a CT sensor (4–20 mA output) and connecting it to an IoT gateway analog input, it is possible to grasp the state of motor from the measured current value. With signal tower operation circuits for machine equipment, connecting an IoT gateway digital input allowed the driving status to be understood.
Further connecting an IoT gateway serial communication to the machine equipment CNC allowed collection of operating data. Sensor information with different interfaces like these all gathers in the IoT gateway.
Because the IoT gateway has a built-in OPC UA server function, it is possible to perform direct communication with the OPC UA client on the host network. The built-in web server function allows for easy monitoring without a specialized server device or visualization tool.
System Monitoring and Process Control in Multiple Facilities Using the Cloud
Visualization of a factory using the IoT allows for the construction of a system with a high degree of freedom,
with features such as the ability to gradually enhance functions after starting out with specific issues you want to solve (everything from small-scale demonstration experiments to coordination of information for the entire company) and a fixed budget on what you can spend.
Here at CONTEC, we are providing the “CONPROSYS HMI System” (CHS) as a piece of SCADA software to easily facilitate construction and operation of visualization systems using the IoT.
CHS is SCADA software utilizing the HTML5 web application system. It is easy to install in a cloud environment or on-premise environment server system. All you need is a web browser to perform development or view information.
CHS screen design allows you to create screens using a drag-and-drop function to drag from the browser like in a picture-making program, without any requirement for specialist knowledge or an understanding of programming languages.
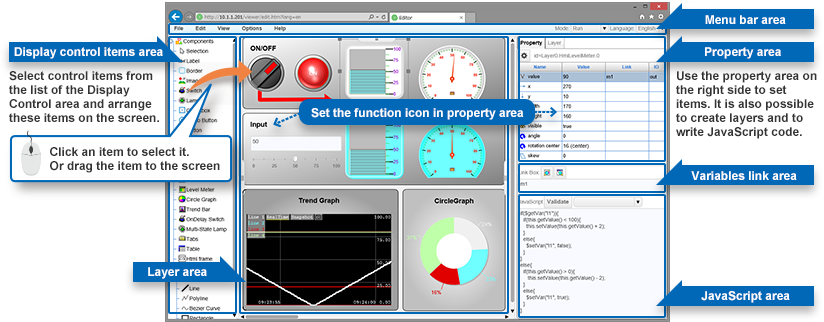
Screens created in this way can be displayed and manipulated in your browser. For example, it is now a simple task to make Andon systems to display production status using a large display, or systems for remote confirmation of the management of production bases in remote locations.
Because it is now possible to realize a bidirectional communication system using MQTT with the equipment side, it is also possible not only to collect operation status data but even to issue commands for remote control output.
By applying this to such purposes as remote operation of unmanned equipment or issuance of control commands to lighting and A/C systems on the factory floor, it is possible to achieve a variety of improvements, including promotion of energy saving activities and creation of a better working environment.
In order to allow operation at the optimum installation cost as befits the scale of the system to be installed, CHS is provided with an annual subscription suited to your project’s scale.
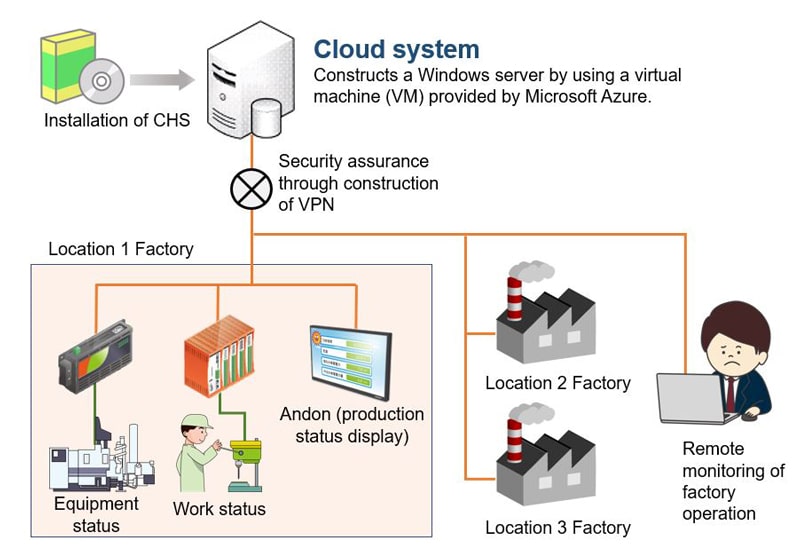 Sample layout of a system utilizing CHS
Sample layout of a system utilizing CHS
In the above example, CHS has been installed and used on a Windows server on a virtual machine provided by Microsoft Azure to manage factories deployed at other locations.
Knowledge Window
“MQTT” (Message Queue Telemetry Transport) is an unsynchronized message protocol that has been made lighter so it can be used in places with unstable network coverage and low-functionality devices. It has a relatively small amount of header information compared to the HTTP protocol, and with a broker coming in and performing communication between the server and the sensor, non-synchronized messaging can be realized. MQTT is a protocol that is well-suited to IoT, and so is widely utilized in systems connected to the IoT.
CONTEC Komaki Factory: A Case Study of Visualization of the Production Process
Needless to say, we at CONTEC have introduced the IoT in our CONTEC Komaki Factory, allowing us to visualize the production process and improve our overall QCD results.
 CONTEC Komaki Factory
CONTEC Komaki Factory
In order to visualize the production process in the factory, the Komaki Factory had to collect various sensor information. Information collected from the sensors is collected and manipulated with the CONPROSYS M2M Controller (IoT gateway) and sent to the CONPROSYS M2M Gateway (Modbus Master). M2M Gateway can collect data with simple settings without any need for programming.
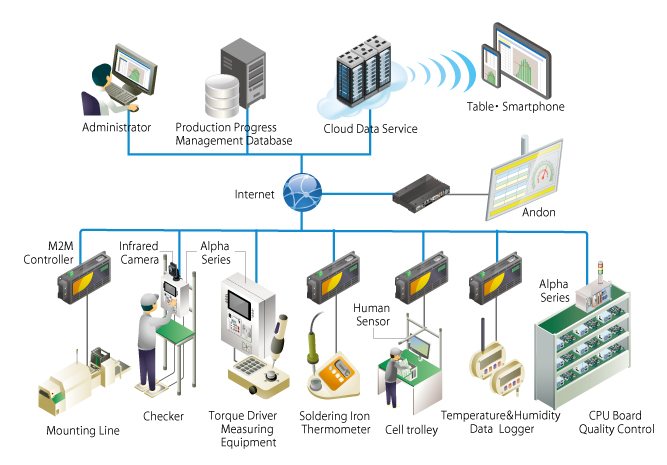
By using the CONPROSYS and M2M solutions product line, complete success has been achieved in visualizing all the data inside the factory: that’s CONTEC Komaki Factory. We are currently promoting productivity improvement to support the manufacture of various types of products by utilizing IoT systems.
CONTEC Solutions for the Utilization of Sensor Information
The CONTEC products used in the case studies and solutions outlined above are compatible with a great many interfaces in order to allow a wide variety of sensors to be used.
By adopting the cloud, data extraction using Web API and data linkage function provided by the cloud system allow both interconnectivity with other systems and smoother system
Related Information
See All Blogs
*
If you have already registered as a myCONTEC member and wish to receive eNewsletters, please change the settings from
"Edit Profile" after logging in.