Electrical equipment and machine tools are used in the manufacture of products. For this reason, safety measures must be taken in case of accidents or malfunctions. In order to implement safety measures, it is important to comply with international standards as well as the laws and regulations set by the respective country. This column provides an overview of safety standards, focusing on international standards defined by ISO and IEC.
Table of Contents
System of Safety Standards
Safety standards can be classified into four hierarchical levels, with the universal international standards at the top. Each standard is harmonized in content by coordinating with higher-level standards. The following diagram shows the four levels of safety standards.
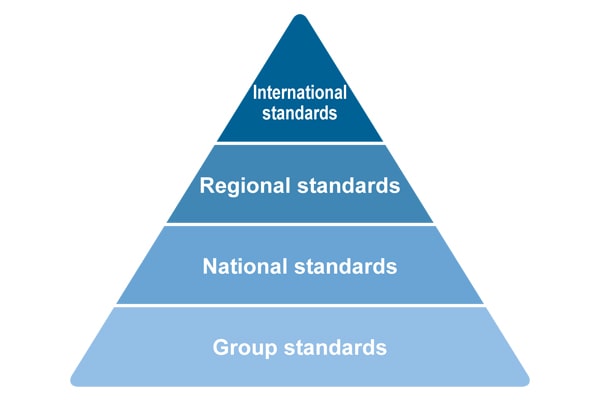
International standards
International standards are standards that can be used commonly by countries around the world. Typical international standardization organizations include
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
- IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
- ITU (International Telecommunication Union), etc.
In recent years, in establishing and revising national standards, it has become mandatory to have consistency with international standards.
Regional standards
These standards are available within a specific region. The EN standards which are used by EU member states belong to regional standards. Examples of standardization bodies include CEN (European Committee for Standardization), which establishes EN standards (excluding those in the electrical and telecommunications fields), and CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization), which issues EN standards in the electrical and telecommunications fields.
National standards
This is the standard used in Japan. For example, JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) in Japan belongs to national standards. Examples of standardization organizations are JISC (Japanese Industrial Standards Committee), which deliberates on JIS standards, ANSI (American National Standards Institute), and BSI (British Standards Institution).
Group standards
These are standards used by certain industry associations. Group standards include standards that are set and used at the level of ministries, industries, companies, and factories. Generally, standards defined in a specific industry are called "group standards" and standards within a company are called "internal standards”.
International Standards (ISO, IEC, ITU)
An international organization for standardization is an organization that sets internationally applicable standards and is established by international agreements. Specific examples include the ISO, ITU, and IEC.
Explanation of international organization for standardization
International organization for standardization: An organization that sets internationally applicable standards, established through international agreements, and is open to participation without restriction by country or region. Examples include the ISO, ITU, and IEC.
From here, an outline of each standard and the system of ISO/IEC Guide 51 and international standards will be presented.
ISO standards
ISO standards are international standards established in 1947 by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which is a reorganization of the ISA established in 1926.
The ISO is a non-governmental international organization in which national standardization organizations participate. The participating standardization organization in Japan is the JISC, which establishes the JIS.
The ISO is responsible for international standardization in all industrial fields (excluding telecommunications), starting with the electrical and electronic fields. ISO standard numbers begin with "ISO" followed by a number and the year of publication.
IEC standards
IEC standards are international standards established by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which was founded in 1906. It has the longest history among the international standards introduced. Like the ISO, the IEC is a non-governmental international organization, and the JISC participates from Japan in the same way as with the ISO.
The IEC is responsible for international standardization in the electrical and electronic fields (excluding telecommunications). IEC standard numbers start with "IEC" followed by numbering using the same rules as the ISO.
ITU-T recommendations
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is an international organization that issues international standards for information and communications. The ITU is divided into several departments as follows.
- ITU-T (Telecommunications Sector)
- ITU-R (Radiocommunication Sector)
- ITU-D (Telecommunication Development Sector)
ITU-T recommendation is a technical standard issued by the ITU-T for wired telecommunications technology. ITU-T recommendations are classified into technical areas from the A to Z series, and the G series (technical standards for communication line transmission systems, transmission media, etc.) and others are particularly well known.
ISO/IEC Guide 51 and the system of international standards
International standards consist of IEC standards for electrical fields and ISO standards for non-electrical fields (machinery, management, etc.). ISO/IEC Guide 51 (Safety aspects-Guidelines for their inclusion in standards) is a set of guidelines for the development of safety standards. The guidelines provide a definition of safety, and by applying the defined requirements to products, they can be harmonized with the technical standards of each country.
The standards are characterized by being systematized rather than independent. Implementing them in combination provides an even higher level of safety protection. They can be broadly divided into the following three categories.
- Basic Safety Standards (Type A standards)
- Group Safety Standards (Type B standards)
- Product Safety Standards (Type C standards)
The following is a diagrammatic representation of the relationship between ISO/IEC Guide 51 and ISO/IEC and the type A, B and C standards.
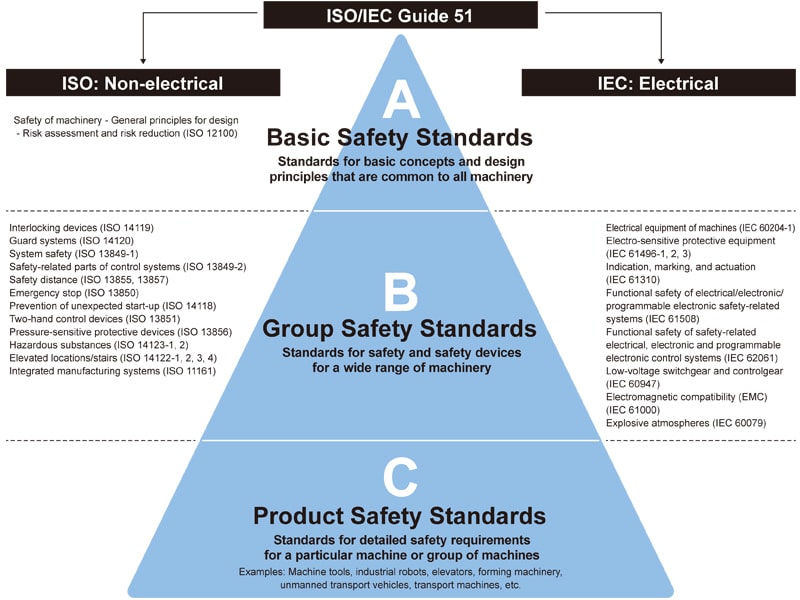
As shown here, by combining safety standards for individual machines from the basic safety standards, we can ensure better omission-free safety.
National and Regional Standards
Safety standards are specified by region and by nation. Consequently, evaluating and checking all of the components during the manufacture of equipment requires considerable time and effort. Products that have been certified in accordance with each of the established standards can use the standard certification mark. This presents the typical safety standards where Contec’s products are certified.
Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law (Japan)
This law was enacted to prevent the occurrence of hazards and injuries/damage caused by electrical products. The law regulates the manufacture and sales of electrical products and encourages the voluntary actions by companies to ensure the safety of their electrical products. There are two categories of electrical products.
- Specified Electrical Products
- Non-Specified Electrical Products
The certification mark also differs as shown below.
Specified Electrical Products are electrical products where hazards are highly likely to arise due to their structure, method of use, and so on. Specifically, the following three types of electrical products are classified as Specified Electrical Products.
- Products used without monitoring for long periods of time
- Products used by socially vulnerable people
- Products used in direct contact with the human body
UL standard (United States of America)
UL standards are product safety standards established by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) in the United States. UL standards standardize the function and safety of materials, equipment, components, and end products. There are two types of UL standard certification systems: Listing certification and recognition certification.
UL standard certification is not required. However, in many cases, individual states in the U.S. require UL certification, and so many electrical products in the U.S. are UL certified.
Search compatible products
CSA standard, C-UL standard (Canada)
CSA standards are safety standards for electrical products and medical equipment in Canada set by the Canadian Standards Association (CSA). The Canadian Standard Association, the group organization of the CSA, is in charge of creating standards, and the CSA is in charge of certification.
The United States and Canada have entered into an international Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA). Consequently, combined certification is possible. Of the marks shown on the left, the top two types are CSA NRTL marks (CSA certified products), which indicate that the product is a UL Listed product that has been tested and certified by CSA. The bottom two types are C-UL Marks (C-UL certified products) and indicate CSA compliant products that have been tested and certified by UL.
Search compatible products
CE marking (EU member countries)
CE marking is a mark that indicates that a specified product sold in an EU member country conforms to the essential requirements specified in EU directives and regulations by the EU for a given field. Products bearing this mark are guaranteed free sale and distribution within the EU.
Many of the essential requirements relate to product safety. However, recently, CE marking has come to be required to declare conformity with environmental performance standards for products defined in the RoHS Directive and other directives.
Search compatible products
Information on the UKCA mark
The UKCA mark is a newly introduced standard conformity mark for products in the UK after leaving the EU. It is used for products in the UK (England, Wales, and Scotland) from 1 January 2021, after the end of the transition period from the CE mark. However, Northern Ireland is not covered by the UKCA mark and requires either the CE mark or the newly introduced UK (NI) mark.
Search compatible products
CCC certification mark
CCC certification refers to the compulsory certification system for product safety in China. The two governing bodies for CCC certification are
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of China (AQSIQ)
- Certification and Accreditation Administration of China (CNCA)
Even if the end product itself is not a compulsory item for certification, if a part is a compulsory item, the product itself is treated as a compulsory item.
Search compatible products
KC certification mark
The KC (Korea Certification) mark is a national integrated certification mark of Korea. This mark is certified by a certification organization designated by the technical standards institute, and the applicable product must be confirmed to be safe and must display this mark. Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of electrical products and broadcast communications equipment that emit electromagnetic waves is the responsibility of the National Radio Research Agency (RRA).
Search compatible products
RoHS Directive
The RoHS Directive refers to the Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council of 8 June 2011 on the Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment.
This Directive was established to restrict the use of chemical substances harmful to the environment and human health at the manufacturing stage of electrical and electronic equipment in order to prevent them from polluting the natural environment. This Directive covers all electrical and electronic equipment in 11 classifications not exceeding a voltage of 1,000 volts AC and not exceeding 1,500 volts DC.
CE marking is mandatory from RoHS2, but if a product is already marked with CE marking under other EU Directives (Low Voltage Directive, Machinery Directive, EMC Directive, etc.), it is automatically considered to be RoHS2 compliant. Therefore, it is important to pay close attention to whether the product with the CE mark complies with the latest directives.
Because the RoHS mark is a self-declaration and not a regulation mark, some manufacturers have devised their own marks to indicate conformity or non-conformity. Contec uses the above marks on its compliant products.

Technical conformity mark
The technical conformity mark certifies that radio equipment complies with the technical standards of the Radio Law (Japan). When applying for a license for radio equipment with the technical conformity mark, the procedure is greatly simplified. Also, wireless LAN and cordless phones for home use do not require a radio station license if they have a technical conformity mark.
Contec Products Compliant with Safety Standards
Contec provides a wide range of products that comply with the safety standards described above. Among them, we offer the GPC-700 Series Global Wireless LAN Unit as a recommended product that meets the standards of various countries around the world.
FA computer (GPC-700 series) compliant with 21 overseas safety standards
The GPC-700 series is an FA computer that supports global expansion into a broad range of countries. The product is compliant with safety standards in Africa, Asia, Europe, Japan, the Middle East, North America, Oceania, and Latin America, and an AC cable that matches the destination country can also be chosen.
Wireless LAN unit with global support
The FLEXLAN FX3000 series is a wireless LAN unit that supports many national standards. This product is available in the following two types.
Two types of wireless LAN units
- Embedded board type FXE3000
- Resin case type FXA3000
Also, the supported countries vary depending on the model. This product is recommended for companies with an active global presence because it covers a wide range of countries in Europe, the United-States, and Asia.
Summary of Safety Standards
This article explained the safety standards required for the manufacture of products. When exporting, it is essential to develop, design, and manufacture products that comply with overseas safety standards.
Contec obtains the safety standards of each country, issues certificates of non-applicability, and provides other services for ensuring safe and secure products, and so please reach out to us about our many products and services.
Related Links
See All Blogs