The Amendment to Japan’s Food Sanitation Act and Methods of Food Sanitation Management Utilizing AI Technology
Under the amended Food Sanitation Act brought into effect on June 1, 2020 in Japan, there is a requirement on the part of businesses handling foodstuffs and the like to perform food sanitation management in compliance with HACCP. This entry will explain the contents of the amendment to the Food Sanitation Act, with particular focus on HACCP sanitation management and the difficulty of sanitation management in the food industry, and methods of food sanitation management that utilize AI technology.
Contents
Contents of the Amended Food Sanitation Act That Came into Effect on June 1, 2020 in Japan

The effect that the amended Food Sanitation Act that came into effect on June 1, 2020 will have on companies consists primarily of the following four points.
- Systematization of sanitation management in accordance with HACCP
- Mandatory notification of health hazard information for foods containing specific ingredients, etc.
- Introduction of the Positive List system for food utensils, containers, and packaging
- Enhancement of safety certification for imported and exported foodstuffs
What Is HACCP?
HACCP is an acronym for “Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points,” an internationally recognized sanitation management method. It is absolutely critical for businesses handling foodstuffs to understand hazards such as food poisoning and the entry of contaminants. The entire process must also be managed so that the hazards can be analyzed so that they can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to tolerable levels so as to ensure product safety.
When a company implements HACCP, implementation must be properly performed throughout the entire organization. The following table lists the 7 principles and 12 steps for implementing HACCP. Steps 1 through 5 are regarded as necessary preparations for implementing Principles 1 through 7.
Businesses with large-scale food factories such as slaughterhouses and poultry processing plants are obliged to implement sanitation management based on the seven principles of HACCP. Even for small businesses, it is required to implement sanitation management based on the HACCP concept. Small businesses manage sanitation using industry-specific guidebooks created by industry groups and approved by Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare.
At the annual FOOMA JAPAN (an international food machinery and technology exhibition), exhibited items included systems and food processing equipment that support sanitation management in accordance with HACCP. In addition to providing information on food machinery, you can know the means of standardization, safety, and sanitation.
Accident Cases Related to Food Safety

Accidents related to food safety occur year after year. For example, on July 21, 2020 in a restaurant in Hofu City, Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan, and then again on August 20 in a ramen restaurant in Tochigi Prefecture, Japan, instances of food poisoning occurred. In both cases, the cause was Staphylococcus aureus, and health centers provided guidance on thorough sanitation management such as cleaning and disinfecting inside and outside the facilities.
If an accident related to food safety occurs, the impact on the business will be immeasurable, with compensation needing to be paid to victims and even business needing to be suspended. In order to prevent incidents such as these, it is important to thoroughly implement sanitation management based on the HACCP concept.
Review Factors for Restaurants and Food Factories
Employee Sanitation Management Training
With the declining birthrate and aging population in Japan, the working population is declining, and the employee base is diversifying, making sanitation management difficult even with just the washing of hands. Due to the regular changing out of human resources through, for instance, temporary employment of part-time workers and the increase in foreign workers with different cultural backgrounds, it is difficult for sanitation management to permeate with conventional methods such as spot instructions and oral or signage-based explanations of procedures.
Introduction of A System That Makes Full Use of AI Technology
In HACCP hygiene management, procedures such as recording visual checks by managers and workers on paper are permitted as before, but paper management tends to be complicated, so if IT is introduced and recording work of critical control points can be automated, it will save time and effort for management and improve work efficiency.
Recently, the trend of applying AI technology to systematize defective product inspections in inspection processes that require visual checks and confirmation of worker behaviors and work procedures is accelerating.
An Era in Which AI Technology Can Be Put to Practical Use
Until now, it has been widely thought that in order to utilize AI technology, it would be necessary to have large-scale systems that can learn and reason with high-performance servers with expensive GPU boards and cloud-type AI services, using massive learning data. Cost becomes an issue when introducing cloud systems and expensive servers that exchange large amounts of data at each store.
It is hoped that the key to solving these problems is edge computing. It is possible to build a practical system that makes the implementation judgment of the inference trained in advance on an edge AI computer.
As an example of a sanitation management system that uses such an edge AI computer, allow us to introduce our hand-washing judgment system that applies AI technology.
Thorough Hand-Washing Guidance with a Hand-Washing Judgment System That Applies AI Technology
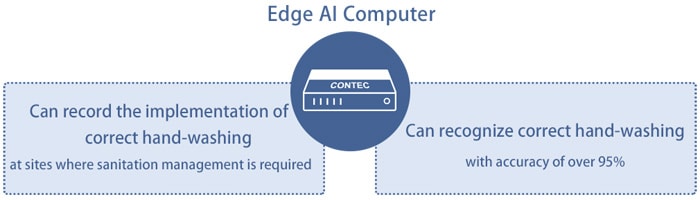
We at CONTEC Co., Ltd., have developed a hand-washing judgment system that applies AI technology and recognizes, by means of AI, the correct hand-washing procedure from images taken with a 3D camera.
The system performs image-processing of the “6 steps of correct hand-washing” recommended by Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, and the AI determines whether hand-washing is being performed correctly. For example, it checks and judges the status of hand-washing with an accuracy of 95% or more, such as whether both left and right hands are being washed, how the soap and disinfectant are applied, and how the hands are washed with the running water.
Since employees can wash their hands while looking at the guidance on the monitor, they can check if there is anything left out, which leads to thorough sanitation management.
The hand-washing judgment system is a solution suitable for restaurants and food factories, where part-time workers and temporary workers frequently come and go and where it takes time to teach hand-washing, as well as for educational and medical sites where guidance on correct hand-washing procedures is required. If you would like to know more about this system, please feel free to contact us.
See All Blogs
*
If you have already registered as a myCONTEC member and wish to receive eNewsletters, please change the settings from
"Edit Profile" after logging in.