Industrial motherboards are important computer components used in factories, manufacturing equipment, medical equipment, public infrastructure, and other applications where reliability is important. However, their characteristics and selection process differ from those of ordinary computer motherboards, and you need to select the right one for your purpose and application of use. In this post, we cover everything from basic knowledge about industrial motherboards to how you can select one.
Contents
What Is a Motherboard?
A motherboard integrates the functions of a computer’s components and plays a central role in the computer’s operation. Critical components such as the CPU and memory are mounted on the motherboard, while external I/O devices such as the power supply and storage devices are connected to the motherboard to enable operation of the computer.
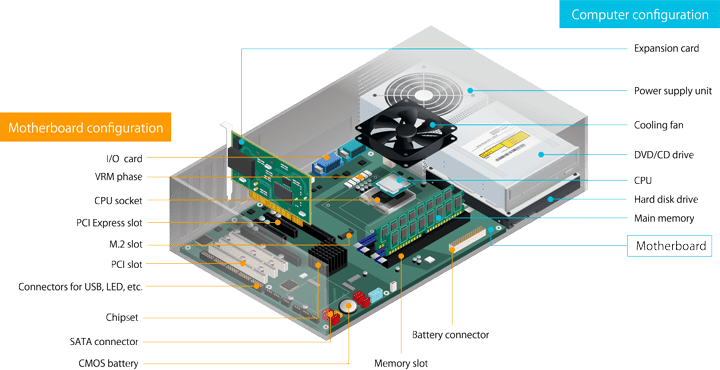
The motherboard enables you to perform data analysis, connect to the Internet, and use applications with AI computing functions, something which has gained attention recently.
Differences between Industrial and Consumer Motherboards
A consumer motherboard is a mass-produced, general-purpose motherboard used for home and personal computers. Industrial motherboards, on the other hand, are used in factories, manufacturing equipment, medical equipment, public infrastructure, and other places where reliability is important.
Features of Industrial Motherboards
Industrial motherboards are characterized by the following four main features.
- Stable long-term supply
- High reliability
- Environmental resistance
- Customizable
Industrial applications require a stable supply of motherboards over a long period of time because the system in which the motherboards are installed will be used over a long period of time. In addition, some industrial applications do not allow shutdowns so the motherboards must be highly reliable. Furthermore, depending on the environment in which they are installed, the motherboards must be able to continue operating under severe conditions such as extreme temperatures, humidities, or vibrations. If an application requires a special connection method or number of slots, the motherboards will need to be customized.
Disadvantages of Industrial Motherboards
On the other hand, industrial motherboards also suffer from the following disadvantages.
Industrial motherboards tend to be more expensive than consumer motherboards because high-quality components are used and because a unique support system is established to create the special designs. Another disadvantage is that the product lead time may be longer because of the low production volume and the inspections involved to ensure reliability.
How to Select a Motherboard
Here are some items to check when selecting a motherboard:
Motherboard Size
Here are the main motherboard sizes:
- Extended-ATX
- ATX
- Micro-ATX
- Mini-ITX
- Pico-ITX and more
Check the features of each size because the size you choose depends on your system’s application and the available space.
For industrial motherboards, size is not the only thing that matters. Other functions and features are also important, especially resistance to environmental stresses and the availability of stable long-term supply.
Processor Family
The processor (CPU) determines the functions, characteristics, and processing power of the motherboard. Select a processor based on your performance and power efficiency requirements. The following shows some of the most common processor families and their features. We will also present the Contec products that use these processor families.
Intel Xeon Scalable Processors
Processors for server computers. Scalable means that you can use high-end to low-end processors on a single platform. Low-end refers to the server applications. To be specific, it means that the CPUs can have several to several dozens of cores (manycore), and you can have multiple CPU configurations such as 1-CPU (1-way), 2-CPU (2-way), and 4-CPU (4-way).
They are used not only for server applications, but also for scientific computing, inference learning, deep learning, and other operations, where the number of threads is critical.
Contec offers a lineup of server-grade FA computers that can be equipped with a Xeon Scalable Processor and a choice of Windows IoT Server as the server OS.
Intel Xeon D Processors
Processors for server computers. These system-on-chip processors integrate the CPU and PCH, a power-efficient platform with a smaller footprint than scalable processors. They can also be used in small server computers, mobile devices, and equipment-embedded applications.
Intel Xeon E Processors
Processors for workstations and entry-level server computers. In industrial applications, they are used for data acquisition servers in factories and for advanced image processing. In general applications, they are used in computers for creative work in images and videos and for hardware/software design and development work.
Contec offers a lineup of workstation-grade FA computers that can be equipped with a Xeon E Processor and a choice of Windows for IoT as the OS.
Intel Core Processors S-series
Processors used in various types of computers, including desktop computers, rack-mounted computers, and embedded systems. They are used in a wide range of applications. Contec also offers a wide lineup of products. Computer manufacturers and news articles sometimes refer to them as Coffee Lake-S, Comet Lake-S, or Alder Lake-S in combination with their development code names.
The processing power is very high even though they are more power-efficient than Xeon processors. A fan motor and heat sink is commonly used to remove CPU heat, but Contec has developed a fanless embedded computer with simultaneous heat dissipation technology.
Intel Core Processors U-series
Processors used in mobile computers such as laptops and notebooks, and fanless embedded computers. Contec also offers a wide lineup of products. Computer manufacturers and news articles sometimes refer to them as Kaby Lake-U or Whiskey Lake-U in combination with their development code names. Contec has developed a thin embedded computer with a thickness of approximately 30 mm with simultaneous heat dissipation technology.
Intel Atom Processors
Intel Processors N-series
Processors used in tablets and small embedded computers. Contec also offers a wide lineup of products. Computer manufacturers and news articles often refer to them by their development code names to distinguish the different generations. (BayTrail, Apollo Lake, Elkhart Lake)
Number of Expansion Slots
Expansion slots can hold additional cards such as graphics cards and instrumentation cards. It is important to check how many and what type of slots are required for the expansion cards you want to use. Slot types include PCI/PCI Express (x1/x4/x8/x16) and more.
Checking the Motherboard Interface
The I/O panel on the motherboard includes Digital Visual Interface (DVI) and High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) output ports for display, USB ports for connecting peripheral devices, and Serial ATA ports for connecting recording media. You need to check the compatible interfaces.
Other Items to Check
Other important items to check include the maximum memory size (ECC memory support), whether RAID is available, whether M.2 slot is available, and the key type.
Conclusions
Industrial motherboards are used in various industries because they are highly reliable and resistant to environmental stresses. However, if you want to take full advantage of their features, it is essential to select the right motherboard. Select a motherboard best suited for your business by determining the size, CPU/chipset, expansion slots, interfaces, and other items to check.
Related Contents
See all blogs